In today’s hyper-competitive market, businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to engage with their customers and drive growth. Beyond offering quality products or services, understanding customer behavior, preferences, and interactions with the brand is paramount. One effective strategy to achieve this is RFM analysis, a data-driven approach that segments customers based on their Recency, Frequency, and Monetary Value.
RFM analysis offers a valuable framework for businesses to identify their Most Valuable Customers and tailor strategies to meet their specific needs. By examining these three key metrics, companies can gain insights into customer loyalty, spending habits, and engagement levels. Recency measures how recently a customer has made a purchase, Frequency indicates how often they buy, and Monetary Value quantifies the total amount they have spent.
RFM analysis is particularly relevant in today’s customer-centric era, where personalization is key. Customers expect brands to understand their individual needs and preferences, and RFM data provides the foundation for creating tailored experiences. By segmenting customers based on their RFM scores, businesses can prioritize high-value users and develop targeted Marketing Campaigns that resonate with their specific interests.
Furthermore, RFM analysis offers numerous benefits for customer retention, a critical aspect of long-term business success. By identifying at-risk customers, businesses can implement proactive strategies to re-engage them and prevent churn.
Additionally, RFM data can be used to reward loyal customers, build stronger relationships, and foster brand advocacy. RFM framework has been known to boost retention rates by 10-20% and increase customer lifetime value (CLV) by 20-30%
In this article, we will delve deeper into the mechanics of RFM analysis, exploring how it works and its applications in customer segmentation. We will also discuss the various benefits it offers for customer retention and how businesses can effectively implement RFM models. Additionally, we will address common challenges that may arise during implementation and examine real-world case studies to illustrate the practical applications of RFM analysis.
RFM stands for Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value—three metrics that help businesses understand how recently a customer made a purchase, how often they buy, and how much they spend.
This analysis enables companies to assign a numerical score to each customer across these three dimensions, usually on a scale from 1 to 5. The combined RFM score provides a holistic view of customer behavior, making it easy to identify loyal customers and those at risk of churning.
RFM analysis begins by categorizing customer data into recency, frequency, and monetary brackets. For example, a customer who made a purchase last week might receive a recency score of 5, while another who purchased six months ago might get a 2.
Similarly, frequent purchasers and high-spending customers score higher in frequency and monetary value, respectively. Once these scores are combined into a three-digit RFM code (e.g., 455 or 322), businesses can divide purchasers into customer groups based on behavioral patterns.
RFM analysis helps businesses answer critical questions like:
By providing clarity on customer behavior, RFM analysis allows businesses to allocate resources more effectively and design engagement strategies that retain high-value users and re-engage inactive ones.
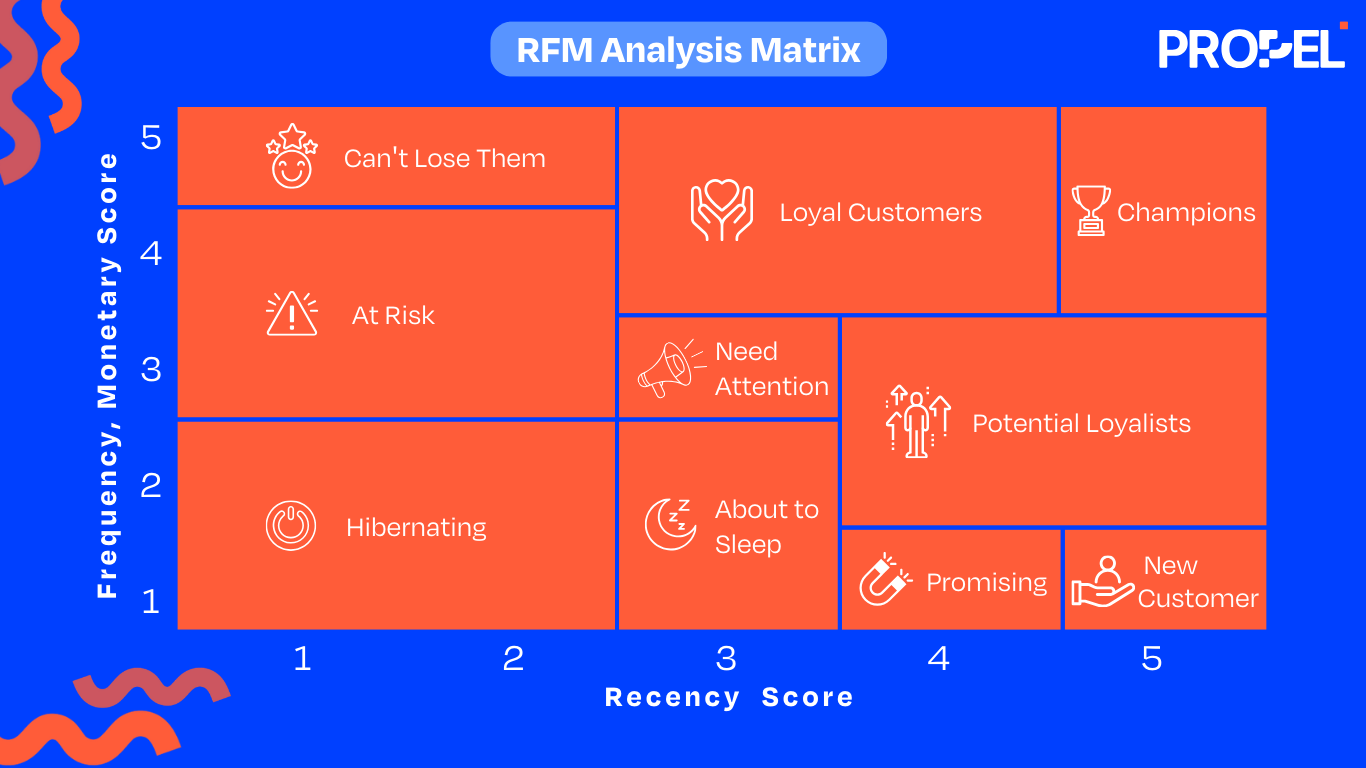
A typical RFM Matrix created based on the three scores
Customer segmentation is the process of dividing customers into distinct groups based on shared characteristics. This strategy allows businesses to tailor their marketing efforts, products, and services to meet the specific needs and preferences of each segment. By understanding customer behavior and preferences, companies can optimize their marketing spend, improve customer satisfaction, and drive revenue growth.
RFM segmentation is one of the most effective ways to categorize customers and personalize their journeys.
RFM analysis offers a valuable framework for businesses to identify their most valuable customers and tailor strategies to meet their specific needs. By examining these three RFM metrics, companies can gain insights into customer loyalty, spending habits, and engagement levels.
RFM analysis helps businesses divide customers into actionable segments, enabling targeted marketing strategies. Segmentation is typically represented through an RFM score matrix, where scores between 111 and 555 reflect varying degrees of Customer Engagement.
Some typical segments include:
By understanding these segments, businesses can develop targeted marketing campaigns, personalized offers, and tailored customer experiences. For example, they can offer exclusive promotions to Champions, provide win-back incentives to Lost Customers, and send targeted re-engagement emails to At-Risk Customers.
Customer retention is the practice of keeping existing customers engaged and loyal to a brand. It is often more cost-effective to retain existing customers than to acquire new ones. By focusing on retention, businesses can build long-term relationships, increase customer lifetime value, and improve profitability.
RFM analysis offers a valuable framework for businesses to enhance customer retention. By examining the Recency, Frequency, and Monetary Value of customer interactions, companies can gain insights into customer loyalty, engagement levels, and potential churn.
RFM analysis provides businesses with early warnings about disengaging customers, allowing timely interventions. By identifying customers with declining recency or frequency scores, businesses can launch re-engagement campaigns, such as offering discounts or exclusive deals, to rekindle interest.
Personalization goes beyond names in emails—it involves sending offers that align with user behavior. For example, customers with high monetary value but declining frequency might respond well to exclusive access to premium products or personalized thank-you notes. RFM analysis ensures that businesses direct their marketing budget where it has the highest impact.
By leveraging RFM analysis, businesses can develop targeted retention strategies that foster customer loyalty, improve customer satisfaction, and drive long-term success.
To effectively implement RFM analysis, businesses need to gather the necessary data, select appropriate tools and methodologies, and interpret the results accurately.
To build an RFM model, businesses need access to purchase history, including transaction dates, purchase frequency, and total spending per customer. This data is typically extracted from Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, e-commerce platforms, or loyalty programs.
Many businesses use tools like Excel, SQL, or Python scripts to conduct RFM analysis manually. However, for more advanced use cases, BI tools like Power BI and Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) offer automated RFM analysis and visualization. These tools can streamline the process, provide deeper insights, and integrate RFM analysis with other marketing activities.
Interpreting RFM scores requires looking at the segments holistically rather than focusing solely on individual metrics. For example:
Additionally, it is essential to consider the specific context of your business when interpreting RFM results. Factors such as industry, customer lifecycle, and marketing goals can influence the significance of different RFM segments.
By following these steps and leveraging the insights from RFM analysis, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their customers, optimize marketing efforts, and drive long-term growth.
While RFM analysis is a valuable tool for customer segmentation and retention, it is not without its challenges and limitations.
To overcome these limitations, businesses can:
By addressing these challenges and limitations, businesses can maximize the benefits of RFM analysis and develop more effective customer retention strategies.
RFM analysis has proven to be a valuable tool for many businesses across various industries. Here are a few examples of companies that have successfully implemented RFM models:
Amazon, one of the world’s largest online retailers, extensively uses RFM-based models to recommend products to its customers. By analyzing customers’ recent purchases, browsing behavior, and other relevant data, Amazon can provide highly personalized recommendations that increase the likelihood of additional purchases.
Sephora, a beauty retailer, leverages RFM insights to create targeted loyalty programs for its customers. By identifying high-value customers based on their RFM scores, Sephora can offer exclusive discounts, personalized product recommendations, and other benefits that encourage repeat purchases and foster customer loyalty.
The implementation of RFM analysis has yielded significant results for both Amazon and Sephora:
These case studies offer valuable lessons for businesses considering RFM analysis:
By following these guidelines and leveraging the power of RFM analysis, businesses can unlock valuable insights, improve customer retention, and drive long-term growth.
RFM analysis is a simple yet powerful framework for customer segmentation and retention. By focusing on recency, frequency, and monetary value, businesses can identify their most valuable customers, predict future customer behavior, forecast churn, and develop personalized strategies for engagement. Businesses using RFM analysis can achieve up to 300% higher response rates and increase campaign effectiveness by up to 50%.
While RFM analysis has limitations, such as the lack of insight into why customers make decisions, it remains a critical tool for understanding behavior patterns. The key to maximizing the potential of RFM analysis lies in its actionability—businesses must continuously monitor, adjust, and act on insights to maintain relevance and value for their customers. Additionally, by combining RFM data with other behavioral and demographic information, companies can create even more effective marketing campaigns.

Ruturaj Bargal is a martech expert and the founder of Propel, specializing in transforming customer lifecycle marketing for consumer brands. With over a decade of experience, Ruturaj has consulted for more than 100 businesses worldwide, including major brands like Xiaomi and Airtel, optimizing their martech stacks to drive effective customer engagement and retention. His work at Propel centers on creating innovative, results-driven strategies for lifecycle marketing.
Got Questions? We Have Answers!
It’s a segmentation strategy that evaluates customers based on Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value of their purchases.
It helps identify valuable customers, optimize marketing strategies, and improve retention by tailoring campaigns to specific segments.
By targeting disengaged customers with re-engagement campaigns and rewarding loyal customers, it reduces churn and boosts loyalty.
Segments include Champions, At-Risk Customers, Loyal Customers, and Lost Customers, each with targeted strategies for engagement.
Challenges include handling low-frequency purchases and limited context on purchasing motives, which can be mitigated with complementary data sources.


Propel specializes in customer lifecycle marketing, helping consumer brands boost retention & reduce churn with tailored strategies and our AI-augmented platform, AURA.
Book a call with our experts and get started today!